We have less than two months left of the GrowSmarter project and it is time to look ahead. When we started the project, Stockholm was already growing fast and needed smart solutions for the growth to be sustainable. This growth has only accelerated and 140 000 new apartments and 280 000 new inhabitants are expected by 2030. Combined with the goal of becoming fossil-fuel free in 2040 Stockholm faces some challenges, but are there answers to find in the GrowSmarter project?
Actually, there are. Quite many indeed.
Better use of urban space
One of the first issues of growth is the use of land and city space. We need to use urban space very wisely. Let’s start with waste. What space is necessary for different waste handling methods. The numbers below are from a Swedish study where a waste collection system sorting into three fractions for 1700 households was evaluated:
| Waste collection and land use per household | Waste collection land use for 140 000 new apartments | |
| Conventional bin system | 0,93 m² | 130 000 m² |
| Conventional automated waste collection system | 0,17 m² | 24 000 m² |
Then we have Envac’s smart waste handling system in Valla Torg. It is collecting 4 fractions, but all in one and the same inlet depositing into one terminal (container). So we collect four fractions and use one third of the space of the conventional AWCS evaluated above. This means that we use less than 0,06 square meters of land per household which would “only” total 8 000 square meters for all new inhabitants expected in Stockholm. Stockholmshem, the housing company, is currently building 160 new apartments near Envac’s smart waste system, and they only need to install the inlets as the terminal can easily handle the waste from these new households.
The same principle applies to the green parking index. The electrical car and cargo bike pool can provide mobility services to inhabitants using only a fraction of the space needed by private cars. Already deployed in Valla Torg, these mobility solutions are also available for the 160 new households thus minimising the need for parking space in the new buildings. This saved parking space alone can pay the additional costs of these mobility services. These are two great examples of smart sustainable solutions which also helps a growing city using its valuable space wisely.

Re-using and storing power
We also need to heat up these 140 000 new apartments. In Stockholm, most buildings are connected to the district heating system. Stockholm Exergi has proved in GrowSmarter that waste heat from data centers or supermarkets can heat up buildings. In 2018 these and other waste heat sources heated up 31 000 apartments. The ongoing installations alone can heat up an additional 27 000 apartments in Stockholm. That means almost 60 000 apartments are heated up with heat that used to go to waste. With the expansion of data centers in Sweden it is not a far-fetched idea that all the 140 000 apartments could be heated with waste heat from data centers. There are data center providers which build their data centers under ground, thus not taking valuable space above ground, but still providing waste heat to the district heating system.
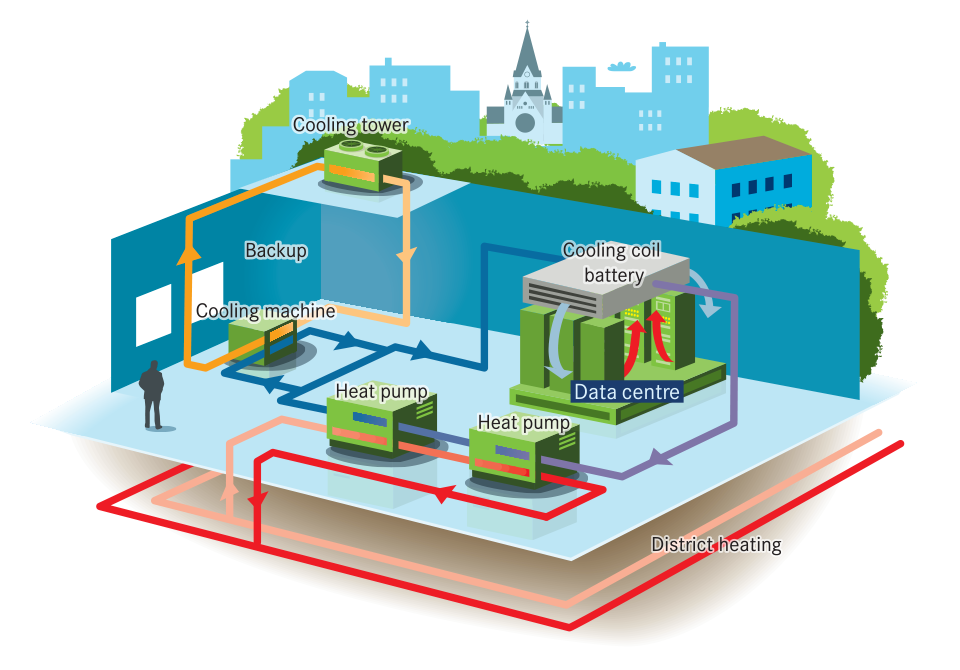
Stockholm still needs to reduce the need for heat in buildings. Skanska showed together with Stockholmshem and L&T that it is possible to reduce the energy need in existing buildings up to 75%. On a larger scale, Stockholmshem found, it is economically feasible to reduce energy use in existing buildings with the solutions installed in Valla Torg by 50%. Combining waste heat recovery with energy efficient refurbishment is one approach that could help Stockholm phase out the last coal and oil used in district heating well before 2030.
Stockholm, as many other cities, is facing an increased electrification. More data is processed, or should I say more and more videos are uploaded, shared and streamed, which demands more data centers. Data centers already consume as much electricity as the UK and this is rapidly increasing. In addition we have the electrification of vehicles and the use of heat pumps also demand electricity. We need to consider that Sweden is phasing out nuclear power, which means that we will be more dependent on renewable energy sources. As the sun doesn’t shine and the wind doesn’t blow all the time, we need electricity storages more in the future than now. L&T has combined photovoltaics, smart electricity management and battery storage in commercial, residential and office buildings in GrowSmarter. Even if battery storage currently is not economically feasible it will be increasingly so in the future. Battery storage can be used in two ways. In summer you store the overproduction of solar electricity there and in winter you cut electricity effect peaks with the storage. The latter is already done now, but will be even more important in the future. The results from the private condominium Årstakrönet where L&T has managed these solutions is very promising as the amount of electricity from the grid could be reduced with more than 30% with these and electricity saving measures. Peak loads have also been shaved and the three phases are no longer running a risk of being overloaded for instance when electrical vehicles are charged.
Streetlights are also abundant in Stockholm with more than 150 000 of them all running on electrictiy. The smart street lights installed show that electricity can be reduced between 20-45% compared to traditional LED-lights. The Traffic Department of Stockholm is now working to find the best solution and open platform to upscale the solutions and are testing this in Stockholm.Lastly the increased population will mean more people and more goods on the streets of Stockholm. As we do not have the space or possibility to build new streets and roads, we need to use the existing infrastructure in a much more efficient way.
Smarter solutions for a connected city
The construction logistics center implemented by Carrier is one such solution. When the construction material needed the day after is transported to the construction site the evening before, we can move these transports from times with a lot of traffic to times with less traffic. The waste can also be collected at the site with the returning transport in the evening. The overall traffic to the construction site will also decrease with the construction logistics center and these transports can be made with vehicles using biofuels as was done by Carrier. Considering that 140 000 apartments need to be built, the amount of construction material traffic will be high the next ten years and it will be important to implement this type of solution widely in the city. Interestingly, studies show that of the heavy transports in a city almost 30% are waste transports. The Envac waste solution mentioned above not only needs less space, but also reduced waste transports in the area with 90%.
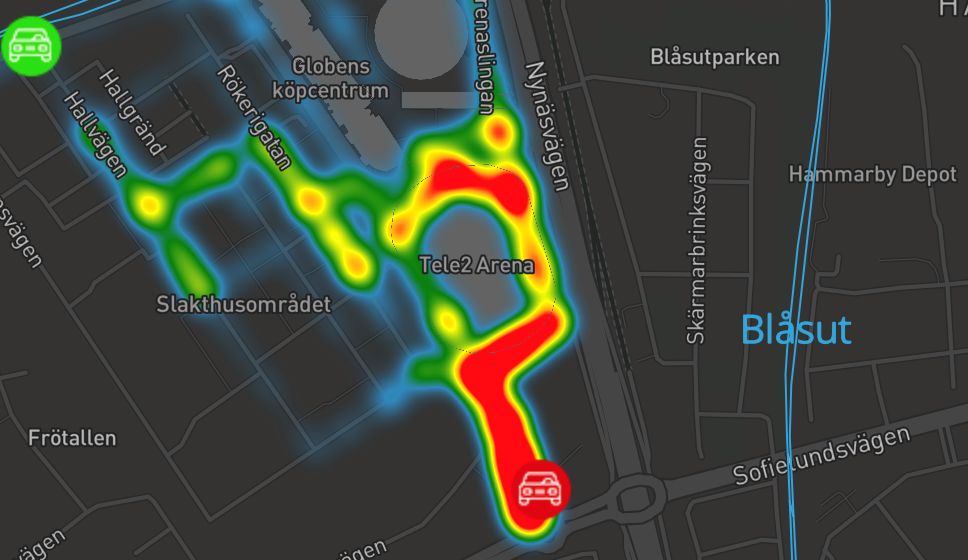
Sensor technology, connectivity, big data combined with artificial intelligence are means by which the city better can manage traffic flows in a city. In the Slakthus-area, the city together with IBM can show traffic flows of vehicles, pedestrians and bicyclists in real time. We can predict congestion, we can understand how weather or different type of events correlate with people and traffic flows in the streets. We can use this information to guide people to transport themselves to and from the area in a sustainable, yet faster, way. As the Slakthus-area will be a large construction site the coming 10 years this information is essential to understand how construction transports, goods transports, event visitor traffic and other traffic can be managed in the often narrow streets. The new subway station will for instance guide a very large flow of people into Rökerigatan, which will be a main commercial street in the area. This street will not have separate pavements or bike lanes, so all modes of traffic needs to share the same street. By predictive flow analysis, especially regarding events, it is possible to manage goods transports and deliveries, so that they do not collide with people going to events.
If this sounds at all interesting I do welcome you to follow our final conference on December 3rd, where all these solutions will be showed as part of the study visit programme. If you have not signed up for the event, you can stay updated by following GrowSmarter on Twitter.
 Mika Hakosalo
Mika Hakosalo
Site Manager, Stockholm
For the previous blog post, click here



